RF Diffusion Symmetry Config¶
Provides interface for passing symmetry configuration to the RF Diffusion node, enabling advanced control over symmetric protein complex generation.
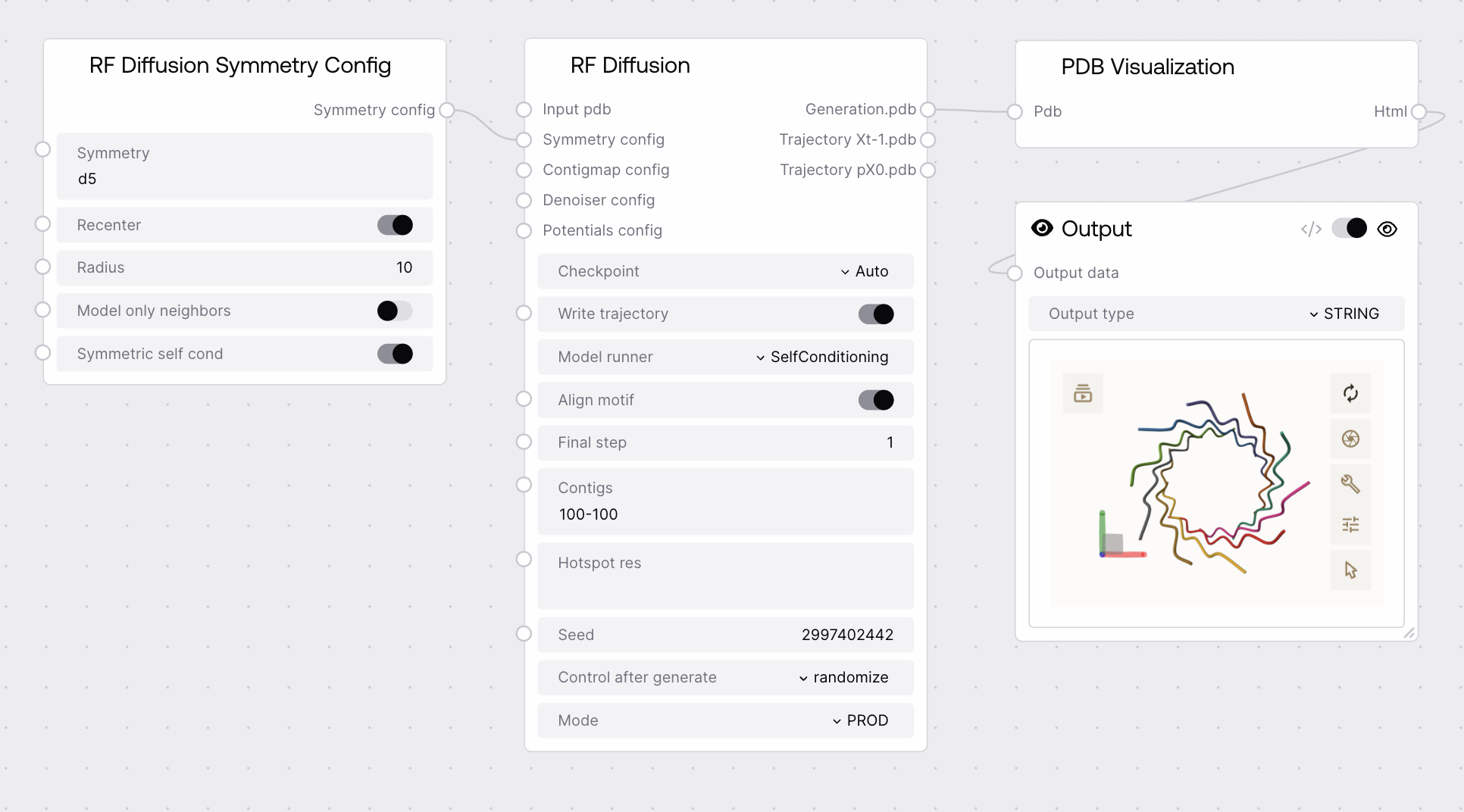
Quick Start¶
- Add the RF Diffusion Symmetry Config node to your workflow.
- Set the desired symmetry type (e.g., c2, d5, tetrahedral).
- Adjust radius and other parameters as needed.
- Connect the output to the RF Diffusion node's symmetry_config input.
Setup Guide¶
1. Insert Node¶
- Drag the RF Diffusion Symmetry Config node into your workflow.
- Connect it to the RF Diffusion node where advanced symmetry is required.
2. Configure Parameters¶
- Choose the symmetry type (e.g., c2 for cyclic, d5 for dihedral, or polyhedral types).
- Set the radius and other options to match your design goals.
Basic Usage¶
Symmetric Protein Generation¶
- Use to enforce cyclic, dihedral, or polyhedral symmetry in generated protein complexes.
- Adjust radius to control subunit placement.
- Enable or disable recentering and self-conditioning as needed.
Configuration¶
Required Inputs¶
| Field | Description | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| symmetry | Type of symmetry to sample. Accepts cyclic (e.g., c2), dihedral (e.g., d5), tetrahedral, octahedral, or icosahedral. | STRING | c2 |
| recenter | Whether to reposition the complex so its center aligns with the origin. | BOOLEAN | True |
| radius | Distance from symmetry center to subunit positions. | INT | 10 |
| model_only_neighbors | Model only neighboring subunits of the asymmetric unit. | BOOLEAN | False |
| symmetric_self_cond | Enforce symmetry during intermediate diffusion steps. | BOOLEAN | True |
Optional Inputs¶
None
Outputs¶
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| symmetry_config | Configuration dict to be passed to RF Diffusion. | {"symmetry": "c2", ...} |
Best Practices¶
Symmetry Selection¶
- Use cyclic (cN) for ring-like assemblies, dihedral (dN) for double rings, or polyhedral types for complex symmetries.
- Validate that the chosen symmetry matches your biological or design intent.
Parameter Tuning¶
- Adjust radius to avoid steric clashes between subunits.
- Enable recentering for better coordinate alignment in downstream analysis.
Troubleshooting¶
Common Issues¶
- Invalid symmetry type: Ensure the symmetry string matches accepted formats (e.g., c2, d5, tetrahedral).
- Unexpected geometry: Adjust radius or check input structure for compatibility with the chosen symmetry.
Need Help?¶
- See the RF Diffusion documentation for more details on symmetry configuration.
- Contact support for further assistance.